A study based on a recent collaborative investigation with Professor Hirasawa of the, Tohoku University Graduate School for a pharmacy graduate course on lifestyle-related disease treatment, has shown that Maitake mushrooms may have the potential to reduce allergy symptoms.
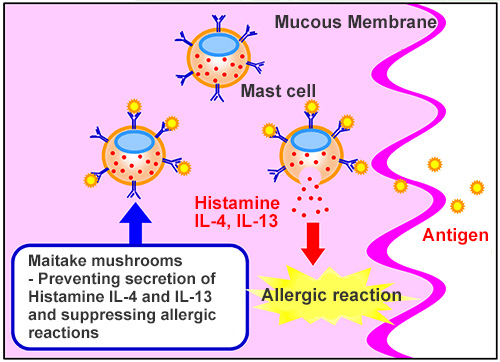
Effect of the action of the mast cells and Maitake
When Antigens, such as pollen, invade the human body, via a mucous membrane, mast cells secrete histamines and cause an allergic reaction.
At the same time, mast cells secrete inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13, and activate immune cells surrounding it to promote inflammation.
In this study, it was revealed that Maitake mushrooms, in combination with the secretion of histamines from mast cells, control gene expression levels of IL-4 and IL-13. In other words, they have the potential to act as an anti-inflammatory agent.
Experimental method
In this experiment, we used a fat soluble ingredient which extracted the ethanoic extract of each mushroom in ethyl acetate.
We then added the extract of each mushroom to a rat-originated mast cell line (RBL-2H3) and performed antigen stimulation in a culture for 20 minutes.
For the experiment, we used DNP-HSA (dinitrophenyl – human serum albumin) as an antigen.
After 40 minutes of antigen stimulation, the Histamine density in the culture fluid was measured; 4 hours later, IL-4, which is an inflammatory cytokine, and IL-13 were measured to ascertain their expression level.
Experimental result
Mast cells given Maitake extract in advance significantly restrained the histamine secretion amount after antigen stimulation.
In addition, the gene expression level of IL-4 and IL-13 of inflammatory cytokine was significantly controlled.
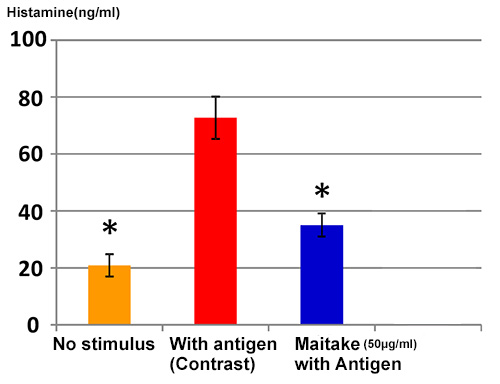
Histamine secretion amount after antigen stimulationn=3, *There is a significant difference between the contrast.P<0.01
The above results show that Maitake mushroom extract can be expected to improve the symptoms of allergic reactions, such as hay fever.
The above results of the study were presented at the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 133th Annual Meeting (2013)

